Review Data from User’s Perspective with Real User Monitoring
It’s all about the user! Real User Monitoring RUM, unlike synthetic tracking, is able to give businesses better insights into what the actual users are experiencing when they are browsing and interacting with web pages.
Especially when Interaction to Interaction to Next Paint is fast becoming the next new big thing, SEO enthusiasts can benefit from field monitoring tools like RUM.
Read on to find out more about what RUM is!
What is Real User Monitoring?
Real User Monitoring is a quantitative measurement system aimed at estimating the quality of user experience based on her/his network connectivity, page loading times and interactivity with specific online services such as e-commerce shops or web-apps.
Although RUM is sometimes thought of as real-time user monitoring, we don’t actually have to monitor the connection or users in real-time. In fact, RUM is a browser real-user monitoring that tracks the resources that are reported by the browser.
Most companies already do have a system or process whereby they collect logs and data about the images that they transform and the time it takes to complete these transformations. However, many businesses are not aggregating the data. The thing is even if companies spend time collecting all the data, but no efforts are placed on ensuring that they are filtered, processed, and organized, these huge statistics and data won’t make any sense for the business.
Real user monitoring vs Synthetic monitoring
Another big question that companies wonder about is, what is the difference between real user monitoring vs synthetic?
Real user monitoring (RUM) is actually the flip side of server-side monitoring. It is a performance monitoring technique that gathers specific information about how a user interacts with an application. Simply put, RUM is all about really looking at our customers, users, and what they see from their site, from their perspectives.
In comparison, synthetic monitoring uses lab tools to fabricate what users MAY have experienced. Such tools include lighthouse npm module, lighthouse user flows, and web vitals extension for Chrome. For companies who really want to “put themselves in the shoes of their customers”, real user monitoring is the way to go.
RUM technologies will help you “travel to the user's device”, the furthest person across the board that's browsing the domain that we are serving to look at their network performance. For example, a user browsing your website from Paris may face different experiences from someone who is surfing it from Japan.
Some questions that RUM will help businesses answer:
- Is the page actually loading quickly for them?
- Are the resources loading in the right order that we want them to load?
- Or is there something that is creating bottlenecks in the entire process whereby a user may be clicking on an image but don’t get a response?
All the above can only be obtained by field monitoring of the devices of users and not lab monitoring.
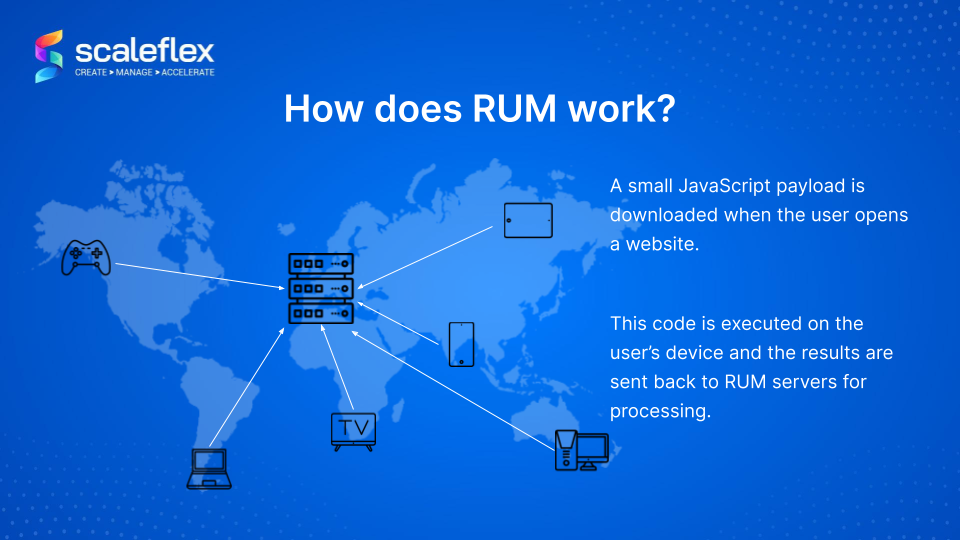
Return to the Table of ContentsHow does Real User Monitoring work?
How RUM works through the use of JavaScript technology to run the codes. The RUM code is downloaded to a user's machine when it is loading resources and all that information stored in the memory with all the timing data is collected by the browser. The collection of data by RUM is not real-time monitoring but actually the monitoring of the browser’s resources.
A side note about JavaScript
JavaScript is the core building block of interactive websites. Just think about the time when you click on a link that changes its color, or a highlight when you input inaccurate data - these are all thanks to Javascript!
JavaScript itself is also responsible for a lot of heavy lifting and generating websites on-the-fly for users. JS detects the size and resolution of the device and decides whether to push this website in a desktop or mobile view. As the mobile view is slightly different from the desktop view, the layout of the webpage is modified as it's being rendered on the device.
As a result, there’s a lot of potential to build very interactive and responsive plugins with JavaScript and all those new technologies that we hear of such as Angular, React, and all those frameworks, they're really based on JavaScript and the ability to run code within a machine that is based on the user's machine.
Debunking the notion of heavy RUM JS scripts?
Even though many SEO enthusiasts will tell you that unnecessary JS scripts would slow down websites, RUM is computationally not a heavy process. This is because as soon as the browser collects a certain number of images, it reports to the JS virtual machine that is running inside - a very lightweight process.
In fact, RUM scripts are similar in size to a medium-sized image. To start collecting the RUM data, 20kb is all it takes.
Challenges of RUM
RUM codes need to be downloaded in the same format, from the same resource and executed in exactly the same way on all the devices in order for it to have accurate data. That means that the greatest challenge is for RUM software to be compatible with all of the device formats and all the technologies.
How is RUM implemented?

To implement the RUM script, there are 3 main options to do so:
- Google Tag Manager: This is the preferred way to do so. Google Tag Manager allows you to customize the pages you want the script to run and when you want it executed. Remember that it is not real-time monitoring, but RUM monitors the resources that are reported by the browser. As such, whether or not the script loads earlier or later, the browser is able to collect all the crucial information.
- Insert Javascript into website’s HTML code: Here, we’re looking at a simple copy and paste. The benefit of such a process is that the hard-coded script will launch instantly when the website loads and it doesn’t pass through a third-party solution.
- Include a URL link inside the website’s HTML: This method tells the consumer’s browser to look for the code at the resource. RUM providers can have the flexibility to update the code remotely.
What data does RUM collect?
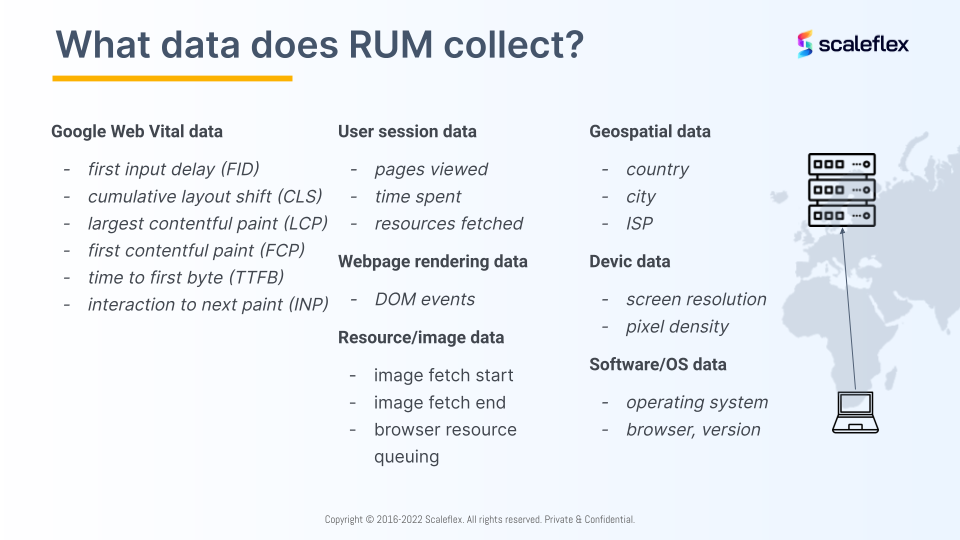
The other question many users may be wondering is to find out what data RUM collects and what can be done with it.
- Google Core Web Vitals Data: Though this data can be found on PageSpeed Insights, Core Web Vitals data is collected by the RUM to ensure a holistic and comprehensive monitoring tool.
- User session data: User session data is created on a simple principle of generating a unique code for a user, based on their IP address. This RUM data analyzes users for businesses and allows companies to track the user journey. The purpose of collecting such data is for analysts to filter out anomalies such as a specific user who has a slow internet connection as such outliers can lead to inaccurate statistics.
- Web Page rendering data: As the browser goes through the process of downloading HTML, it creates milestones like posts with timings. When the browser starts downloading the page, it creates a certain flag and reports whenever it downloads the page accurately.
- Resource / Image data: With every resource downloaded, there’s a start and end time. RUM tracks how long the process took to find out exactly which portion of the website is causing slow load times.
- Geospatial data: RUM data can also help companies segment the users based on their geographical regions to better understand how the web pages load in different parts of the world.
- Device and software data: Just like responsive plugins, RUM has the ability to detect the device data, such as pixel resolution and pixel density, as well as the operating systems the browser uses.
What insights can RUM provide?
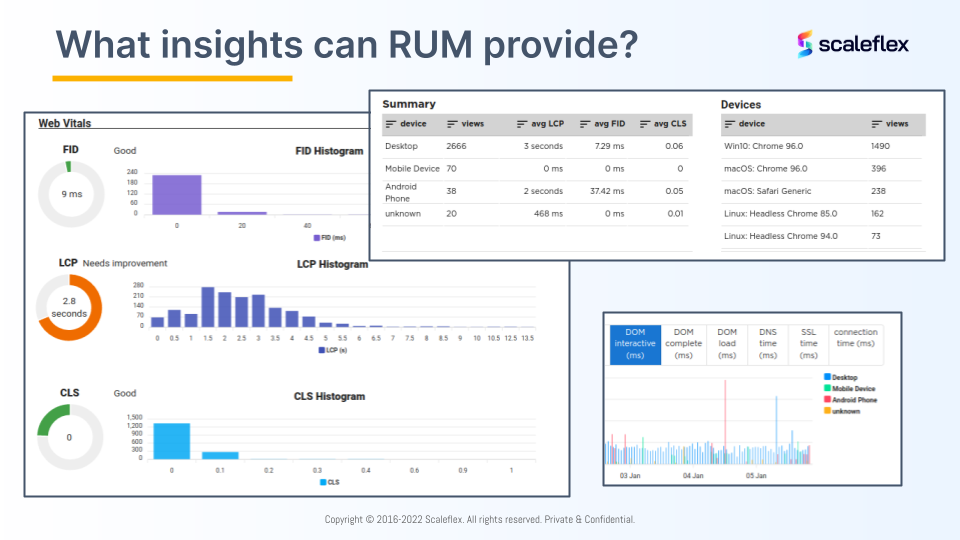
With all that information being collected and tracked, RUM helps companies and brands see what the users actually see. With RUM, website and tech teams can:
- observe how connections, device types and locations affect the browsing experience
- monitor how other resources (CSS, JavaScript, Fonts) impact the image loading performance
Agencies can also make use of such RUM insights to their clients and know exactly what to solve to improve their web performance.
Key Takeaways
Analyzing data and monitoring how their content is doing is always important for businesses if they want to improve their performance and strategies. Whether or not they choose synthetic or real user monitoring really goes back to the goals they would like to achieve.
When Google keeps repeating the same message of: put users first, well, we don’t have to say too much to tell you which type of monitoring will be more insightful.
While basic real user monitoring tools like Google’s PageSpeed insights and Chrome User Experience report can help you get that data, enterprises that want to bring their SEO and web performance to the next level should really invest in real user monitoring software.
Scaleflex is continuously improving its Real User Monitoring tool. Subscribe to our mailing list to gain the latest updates on Scaleflex’s RUM!





