Is Open Source Digital Asset Management Good For You?
Are you considering a Digital Asset Management system? If so, you are probably aware that the pricing for most plans can be rather hefty and high, with annual licensing fees running into the thousands all the time. But there is another option out there, and it's available at a fraction of the cost.
Small and medium businesses often consider software in an open source environment for its lower costs. It allows users to customize the software easily for their company’s needs since the source code is available for anyone to see and modify. But is it suitable for everyone?
What is an Open Source Digital Asset Management Software?
Open-source software has been around ever since the beginning of the Internet. It can be seen as a philosophy that encourages users to participate in designing and creating their products. Today, developers increasingly use it to support their applications. A Gartner survey further supports this as it found that over 90% of its respondents have used open-source software.
A Digital Asset Management open source solution is essentially a DAM that anyone can edit - because the source code is publicly available for anyone to inspect, modify, and enhance.

In other words, a Digital Asset Management system open source software is one that has been created by a community. It comes with APIs to enable integrations with your existing ecosystem. Users can contribute to the product in any way they like; they can build on it, maintain it, and make modifications—and those changes will be available to anyone else who uses the product.
The idea behind open source is that a network of users is more likely to create good products than a single company trying to do everything alone, providing a good alternative to the buy vs build dilemma.
Open-source Digital Asset Management enables companies to streamline content workflows, store and manage digital assets like images, photographs, videos, and documents throughout their lifecycle as the go-to solution to automate the repetitive parts of content operations. It presents a wide variety of possibilities and potential beyond the original creation.
Yet, for the majority, this sounds like a security nightmare. Why would you want to open up your Digital Asset Management software to hackers?
But Digital Asset Management open source solutions don’t mean unsecured — in fact, it can be quite the opposite. According to Linus’s Law, when given sufficient eyeballs, all bugs are shallow. As many people can see the code and make modifications, it's easier to find bugs that bad actors might exploit. And because the source code is publicly available, you’re free to modify the software to fit your own needs.
Especially for companies looking to create, implement, and launch applications and systems for highly specific needs, open-source Digital Asset Management allows for complete customization.
Differences between Digital Asset Management Open Source vs Closed Source solutions
In contrast, closed-source Digital Asset Management solutions offer a way to protect the integrity of your assets in a controlled manner. It is sometimes an in-house system designed and implemented by an organization specifically for use by its personnel and is not publicly available.
Or it could be proprietary software whose source code is not shared. The term "closed source" refers to the fact that access to the system is restricted to those granted permission to use it.
In terms of usage, proprietary DAM usually does not allow for much customization (beyond what is permitted by the vendor) compared to its open source counterparts. Open source Digital Asset Management solutions with free access to the source code offer more flexibility and control over how users store, manage and interact with their digital assets than proprietary DAM, making it easier for integration into a company's environment.

Features and Benefits of Open Source DAM
There are numerous features and benefits of Digital Asset Management system open source solutions.
Cost-Effective: Compared to a proprietary DAM or building one in-house, open source Digital Asset Management software is more cost-effective as it can be used without paying a license fee.
Flexible and Customizable: Some companies don’t need all the features from an out-of-the-box proprietary DAM software, while others may need more functionalities. The open-source environment allows developers to customize or build their very own DAM, saving lots of development time compared to starting it from scratch.
Easy Integrations: The nature of open source Digital Asset Management solutions means that it comes with APIs, making it easy for you to bridge them with any of your existing platforms or ecosystem and enabling a consistent CX across your teams.
Scalable: Changing from one DAM to another can be a considerable challenge, especially for enterprises with a large volume of digital assets. Even if business or content operations change along the way, such as having new forms of digital assets, the open-source DAM allows for such modifications without looking for a brand-new DAM. You can also introduce new features along the way as your company grows.
Faster Innovations: As a digital asset management system open source software encourages a diverse community of talented users to contribute ideas and experiences while using the source code in their products; it brings forth new improvements and advancements at a faster rate.
Community and Vendor Support: Open-source software has come a long way since its inception, and today, open-source vendors are often reliable, well-funded companies which operate like proprietary software vendors, offering high-quality support and products. You'll also benefit from being in a community of like-minded individuals
Limitations of Open-Source DAM
Even though there are significant benefits of open-source DAM, there are also some limitations and considerations companies need to consider when implementing.
Require an experienced IT team: You'll need an experienced team of IT specialists with experience managing and coding Digital Asset Management if you want to take advantage of an open-source DAM platform's coding and customization capabilities. This entails hiring personnel with specific talents and onboarding them for most businesses.
Need security verification: While open-source software is increasingly safer than before, companies need to have dedicated employees to ensure that the digital assets are secure and encrypted. Failing which, may lead to legal and financial costs and reputation damage. These liabilities will need to be considered before embarking on an open-source DAM.
Take into account unanticipated costs: Even though there are numerous plug-and-play software that is open source, businesses will need to take into account unanticipated financial costs that can arise out of a need for more storage, more personnel to fix bugs, just to name a few.
There is no truly free DAM software. Businesses should remember that although there are no license fees involved in using an open-source DAM, storage space is not free.
Who is Open Source Digital Asset Management for?
Digital Asset Management is a solution that helps your company manage and organize numerous media assets to simplify content workflows and maintain brand consistency. While open-source Digital Asset Management systems offer features and benefits not available in off-the-shelf solutions, it isn't quite for everyone. Smaller companies that do not have sufficient in-house resources to run the program or make changes may need to reconsider their strategies.
Then comes the question of who is it really for? There is surely no clear-cut answer to this question. The idea of the cost being a major deciding factor for open source DAM has increasingly been thrown to the back-burner. Instead, other factors have taken centre-stage.
Companies that eventually adopt open-source DAM should have the following:
- an experienced IT team
- highly-specific DAM needs, requiring high levels of personalization
Without these two main factors, you'll be better off with a closed source Digital Asset Management like Filerobot, which offers comprehensive technical support and is flexible enough to develop solutions for your business needs.
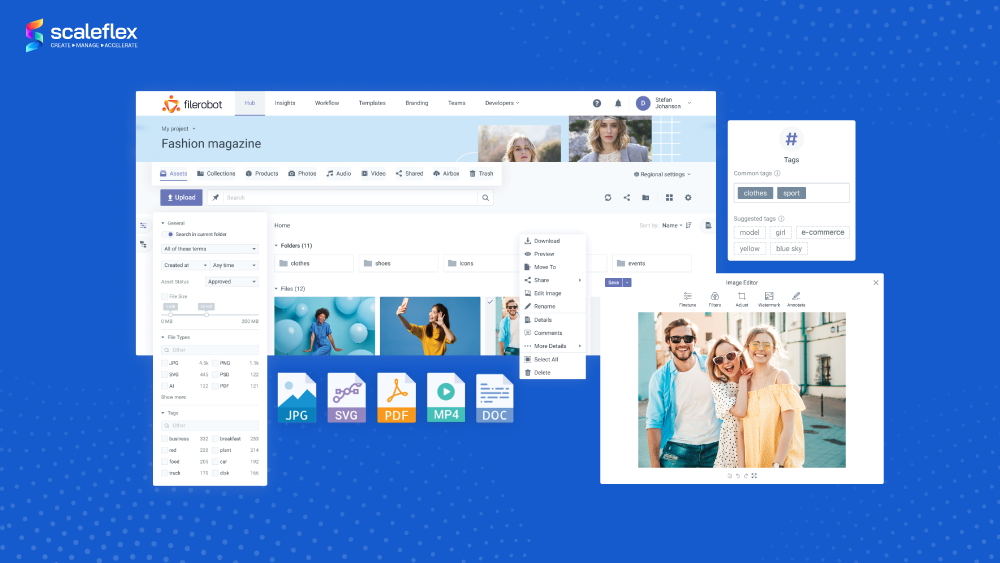
If you like the open-source environment, check out the open source Image Editor plugin! Explore the demo to discover how it works.
Return to the Table of ContentsConclusion
Generally, whether or not your company chooses to get an open source or closed source Digital Asset Management, there is no right or wrong answer - it really depends on the nature and stage of growth of your business. Just bear in mind that the decision for the best DAM software for your organization has long-term implications and thus should be carefully considered.
Still unsure what type of Digital Asset Management solution your company really needs? We invite you to attend a no-obligation chat with our friendly experts!
FAQs
What is an open source Digital Asset Management?
Open-source DAM helps your company manage and organize numerous media assets to simplify content workflows and maintain brand consistency and its source code is publicly available for sharing and modification.
What is a closed source Digital Asset Management?
In comparison, closed source DAM’s source code is not shared and access to the system is restricted only to those who are given permission to use it.
It could be a proprietary system which you’ll need to “buy” to enjoy its features or “build” in-house for your digital asset needs.
Are open source Digital Asset Management made using Javascript?
Since JavaScript is one of the most popular programming languages, 97% of websites are based on Javascript, there will be java-based Digital Asset Management open source software in the market.
Is open source the same as Headless Digital Asset Management?
No, these are two completely different concepts. Though both allow for integrations, open source refers to software (Headless or not) in which the source code is made publicly available. Headless DAM and Headless software could be closed source but how it works is that you get API-access, working without a graphical user interface.
Return to the Table of Contents




