DAM Librarian: Revolutionizing Data Management
In the digital world we live in today, the role of librarians extends far beyond managing physical books and paper documents. Modern librarians, often referred to as asset librarians or digital archivists, play a crucial role in managing and organizing vast amounts of digital data within organizations. For this, librarians often use Digital Asset Management (DAM) systems, which are designed to manage, store, and organize digital resources efficiently.
But this is no surprise: DAM systems were not developed independently of librarians; rather, they were created in collaboration with them. Librarians, with their extensive experience in cataloging and organizing information, have been instrumental in the development of DAM systems. These systems are designed to meet the specific needs of managing digital assets efficiently and effectively.
For librarians, who are increasingly tasked with managing vast collections of digital resources, Digital Asset Management means more than just improved storage capabilities; it represents greater operational efficiency, enhanced accessibility, and streamlined processes. But how was this achieved before the implementation of such systems? Read on and let’s find out together.
Librarians as archivists: Pre-DAM Data Management
Historically, librarians have always been the custodians of information. In the pre-digital era, they managed physical archives, cataloging systems, and manual records. Their expertise in organizing and preserving information laid the groundwork for modern data management practices.
Before the advent of DAM systems, data management relied heavily on manual processes. Librarians used cataloging systems to organize physical items, while early digital solutions were often rudimentary and lacked the sophisticated features of modern DAM systems. Despite these limitations, librarians developed efficient methods to manage and retrieve information, setting the stage for more advanced systems.
The development of DAM systems marked a significant milestone in the evolution of data management. These systems were not introduced to librarians as a new concept; instead, they were developed with the active involvement of librarians. The principles of cataloging and metadata management that librarians had perfected over the years were integrated into DAM systems to create a robust solution for managing digital assets.
Transition to Digital Asset Management
The transition from manual to digital asset management was driven by the need for greater efficiency and accessibility. Librarians played a key role in this transition, leveraging their expertise to adopt and refine DAM systems. This shift involved overcoming several challenges, such as data migration, user training, and resistance to change, but it also meant greater improvement in their methods thanks to key features of DAM systems.
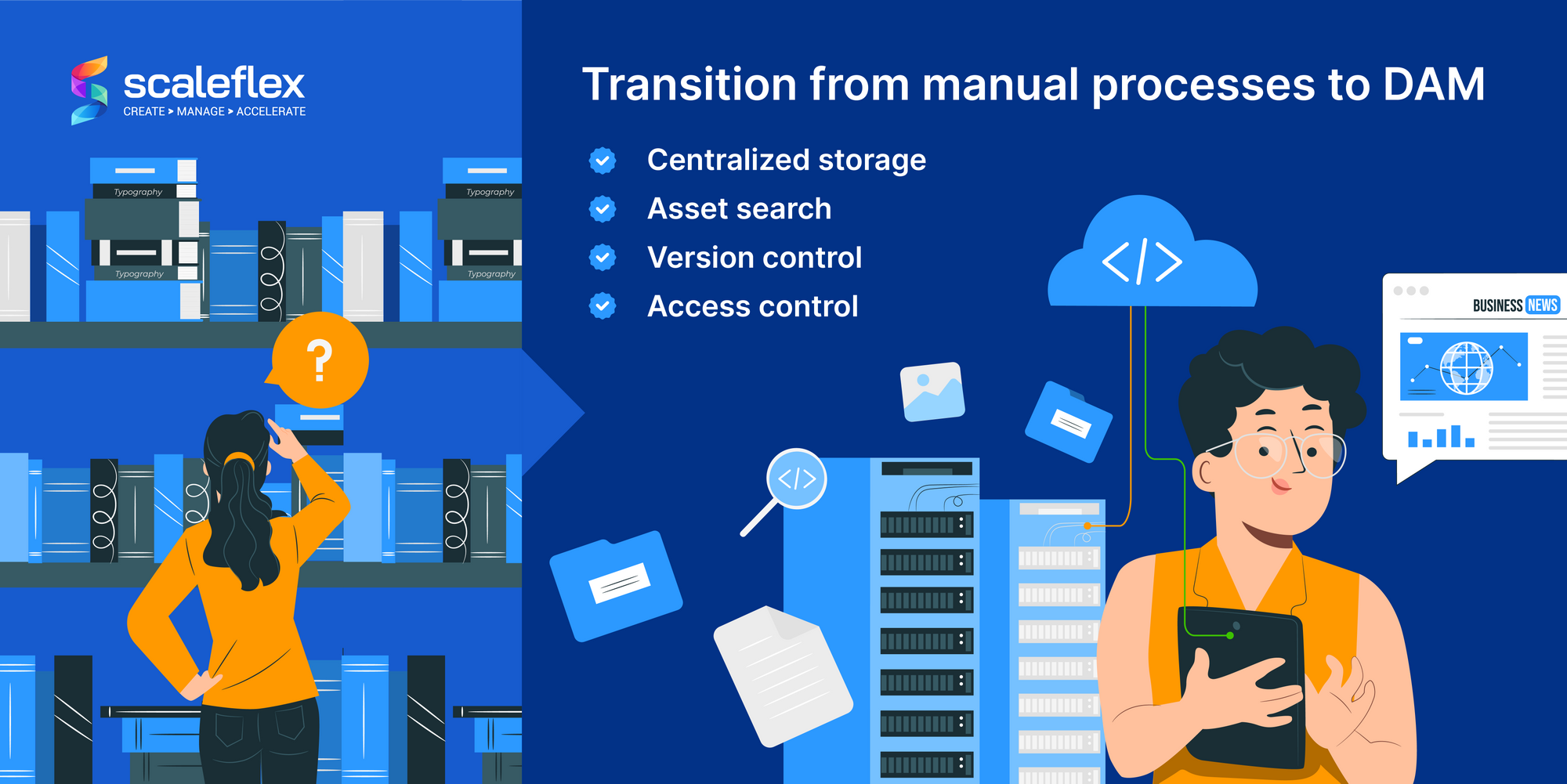
- Centralized Storage: Provides a single repository for all digital assets, making management and retrieval more efficient.
- Asset Search: using metadata, custom tags and intuitive search algorithms, DAM systems provide robust search tools that allow for quick and efficient retrieval of digital assets.
- Version Control: Keeps track of different versions of digital assets, ensuring that the most recent and accurate versions are always accessible. Some DAMs also provide features that avoid duplicates.
- Access Control: Allows a digital asset management librarian to define who can access and modify digital assets, protecting sensitive information and maintaining data integrity.
The evolution from traditional archiving to digital asset management marks a significant shift in how organizations handle information. As organizations transitioned from manual processes to sophisticated DAM systems, the role of archivists has evolved into what we call DAM or Asset librarian. These modern professionals leverage advanced tools and methodologies to manage digital assets more efficiently.
DAM librarians
The role of DAM librarians or asset librarians extends far beyond traditional library duties. These professionals are responsible for organizing, managing, and preserving vast amounts of digital data within organizations.
How? DAM librarians develop and manage metadata and set clear guidelines for data entry, ensuring that all relevant information is systematically captured and organized.
Their responsibilities also encompass setting up and managing access controls to define who can access and modify digital assets, thereby protecting sensitive information and maintaining data integrity. In essence, a digital asset management librarian plays a critical role in the digital age by ensuring efficient data management, facilitating seamless data sharing across the organization, and maintaining the integrity and usability of digital assets through robust metadata governance and digital preservation strategies.
Metadata in DAM
First of all, what is metadata? Basically, metadata is data that describes and provides information about other data. It is often described as "data about data," and it’s crucial for libraries using DAM systems. It facilitates the efficient retrieval and use of digital assets by providing essential details about each item.
For a digital asset librarian, using metadata is key as it allows users to quickly and easily locate the resources they need. This improvement in searchability is crucial in their setting, where the volume of digital assets can be overwhelming without a systematic approach to organization.
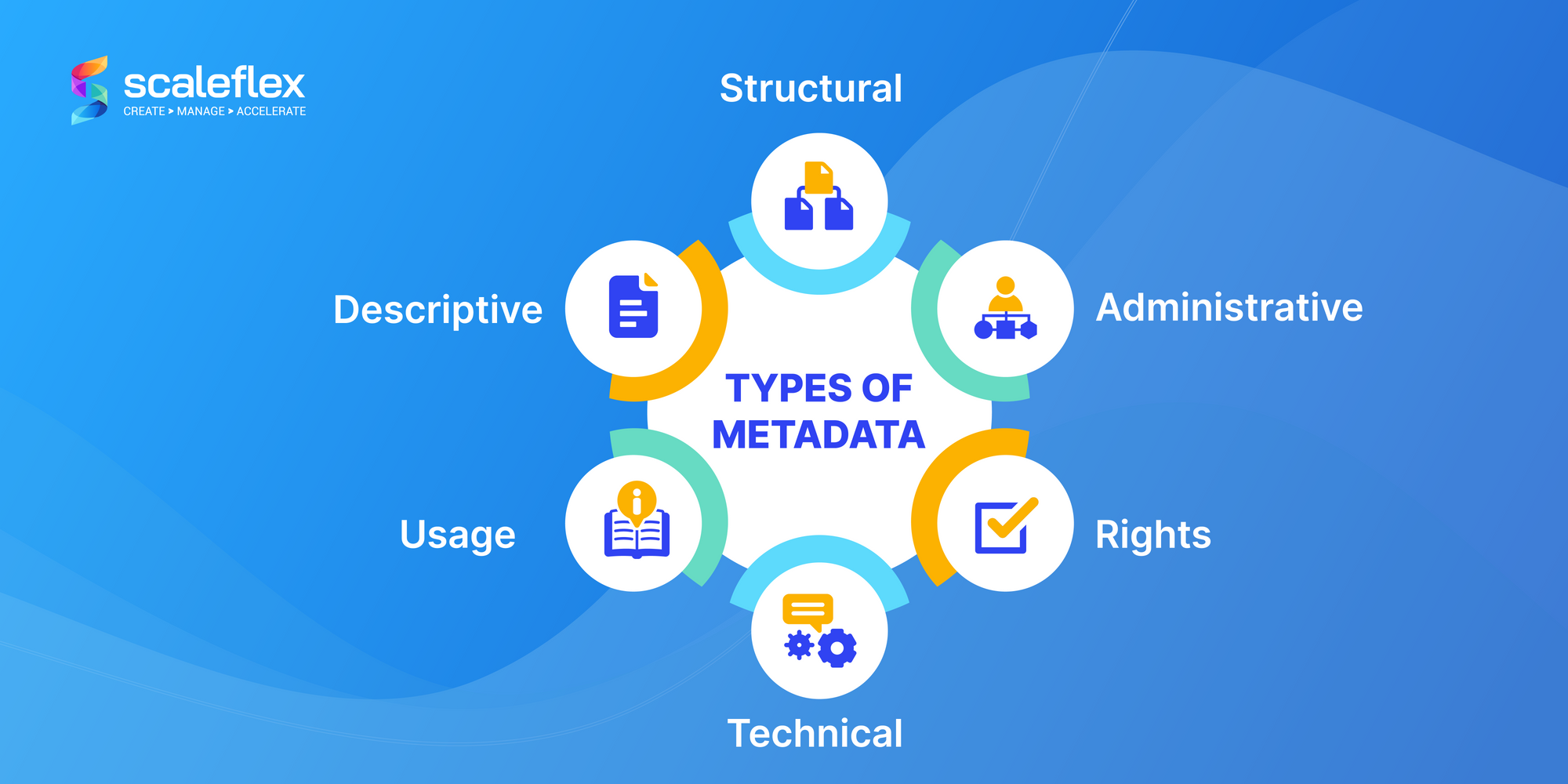
There are several types of metadata that can be applied, each serving a specific purpose, contributing to a comprehensive and efficient management system that meets the diverse needs of library users. These include:
- Descriptive Metadata: titles, authors, subjects, and keywords, which help users identify and locate items within the library's digital collection.
- Structural Metadata: defines the internal structure of digital resources, such as the organization of chapters in an e-book or sequences in a multimedia file.
- Administrative Metadata: contains information related to the management and administration of digital assets, including creation dates, file formats, and custodial history.
- Technical Metadata: provides technical details about digital assets, such as file type, resolution, and software requirements, ensuring proper handling and preservation.
- Usage Metadata: tracks how and when digital assets are used, offering insights into their popularity and utilization patterns.
- Rights Metadata: manages information about the legal rights and usage permissions for digital assets, ensuring compliance with intellectual property laws.
For a digital asset librarian to maximize the benefits of a DAM system through metadata, it is necessary to develop effective metadata schemas.
Metadata schemas
A metadata schema is a structured framework or blueprint that defines the rules and standards for how metadata is described, organized, and managed. Librarians can use established standards like Dublin Core while customizing schemas to fit the specific needs of their collections. Best practices include defining mandatory and optional fields, creating clear guidelines for data entry, and regularly reviewing and updating metadata schemas to maintain accuracy and relevance.
Creating a well-structured metadata schema is the first step towards achieving efficient digital asset management. It provides the foundation for consistent data entry and ensures that all relevant information is captured and organized systematically. This structured approach not only makes the retrieval of digital assets easier but also supports other vital aspects of library operations, such as metadata governance.
Metadata governance
Metadata governance is crucial for maintaining the integrity and usability of the data within a DAM system. For librarians, this involves setting clear rules and standards for metadata creation and maintenance, ensuring that all staff members follow the same procedures. Effective metadata governance facilitates seamless data sharing across libraries and enhances overall data quality, supporting the structured metadata schemas developed earlier.
By implementing strong metadata governance, libraries can ensure that their data remains consistent and interoperable, which is essential for collaborative efforts and resource sharing among different libraries. This governance framework acts as a guide for DAM librarians, providing them with the necessary protocols to manage metadata efficiently and effectively.
Conclusion
The evolution of librarians' roles from managing physical archives to mastering sophisticated DAM systems underscores their crucial contributions to modern data management. As asset librarians or digital archivists, these professionals have not only adapted to but also shaped the development of DAM systems, leveraging their expertise to enhance organizational efficiency and accessibility.
By implementing robust metadata schemas and governance practices, DAM librarians ensure the systematic organization, preservation, and retrieval of digital assets, playing a vital role in the digital age. Advanced DAM systems like Filerobot allow to further streamline these processes, offering modern tools that perfectly meet the needs of librarians.
FAQs
What does a DAM librarian do?
A DAM librarian is responsible for organizing, managing, and preserving digital assets within an organization.
What is metadata?
Metadata is data that describes and provides information about other data. It includes details such as the author, date created, date modified, file size, and more.
What is the role of metadata in a DAM system?
Metadata provides essential details about each digital asset, facilitating efficient retrieval and usage. Different types of metadata, such as descriptive, structural, and rights metadata, help in organizing and managing the assets systematically.
Why is metadata important in DAM systems?
Metadata improves searchability and accessibility, making it easier for users to find and use digital assets.





