Media Upload & Storage: Approaches For Organizing Your Digital Files
Do any of you remember the terror of organizing all your files in the pre-cloud days? The process was complex, to say the least, involving applications copying files to a disc over the File Transfer Protocol (FTP). Sharing data, via email or by foot (like taking the disc to your friend or colleague), often involves size limits regarding attachments. Lastly, the security of it all was a living hell!
Today, we have plenty of media uploaders, file sharing solutions and file uploaders to choose from, like Dropbox and Google Drive, to name just a few. Once a file is uploaded to the specific service, it can be synchronized across different devices, and can be easily shared with others. Furthermore, most vendors offer both desktop and mobile applications, making it effortless for users to upload, store, sync, and share their data.
Companies (from SMBs to large enterprises) also have many great options to choose from, so that they can neatly organize and share their files. This article will introduce you to everything you need to know about media upload, including the variety of available services, such as upload tools and widgets, and use cases.
What Does Media Uploading Mean?
In layman’s terms, media uploading refers to the process of data being sent from a computer to the Internet. Uploading can also mean transmitting data from one computer system to another via a network, with common methods including uploading via web browsers, FTP clients, and terminals.
We should underline that uploading is a broad term, and can be used in the media upload context of many services that send files to a central server. It can also be characterized as sending files between distributed clients, like peer-to-peer file-sharing protocols. There are also multiple cloud services (i.e. Google Cloud) that bring another layer to the subject.
In the context of the Internet, uploading generally means sending files. Various files can be uploaded to various online locations. Media asset files (shortened “media assets”) include images, documents, audio files, videos, in formats, such as:
- Photo file formats, such as JPEG, PNG, GIF, TIFF, BMP, WEBP, AVIF;
- Music file formats, such as AAC, MP3, WAV, WMA, DOLBY DIGITAL, DTS;
- Video file formats, such as MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, AVI, MOV, AVCHD, H.264, H.265, DivX and DivX HD, Xvid HD, MKV, among others.
- Document file formats, such as PDF, DOC(X), PPT(X), XLS(X), TXT, HTM(L)
Who Needs Media File Upload?
That’s a question with many answers! Media upload is something that we all do, both in our professional and personal lives.
According to the specific need and situation, there are various services and platforms to choose from. For someone who wants to send holiday images to a friend, a media upload service that offers an instant upload gallery without registration would be a nice fit. However, small and mid-sized businesses, as well as large corporations and marketplaces, need a bigger and more secure place (and space) to store and organize their files.
That being said, according to the type of use (corporate or personal), there’s a wide range of upload needs. When you upload a video or image to your personal social media account, that’s a media upload. When you upload dozens of images to your online shop… well, that’s also an example of media upload!
Why is Fast And Smooth File Upload Important?
A fast and smooth media file upload process is crucial for companies, as it can save a lot of time. Of course, it serves you well in managing your personal accounts and deeds, too.
Using a fast uploader can significantly cut the time needed for the entire process. If you don’t have adequate service at your disposal, you’d most likely need to perform several steps, including analyzing the sizes of your media files, cutting the large ones into smaller pieces, and finally compressing them. Sometimes, slow internet connections can also add more time to this rather complicated activity. So, to save time and effort, choose your service wisely!
Where Can You Upload Media Files?
Below you will discover the services that provide the option of media upload – file transfer, cloud storage, DAMs and CMS. Make your choice according to your needs, and first, answer these questions:
- Is your demand related to personal or professional tasks?
- If you are looking for a professional solution, do you need to make a choice for an SMB or a larger enterprise?
- Do you need customized features?
Find useful details about each of the listed services in the following paragraphs
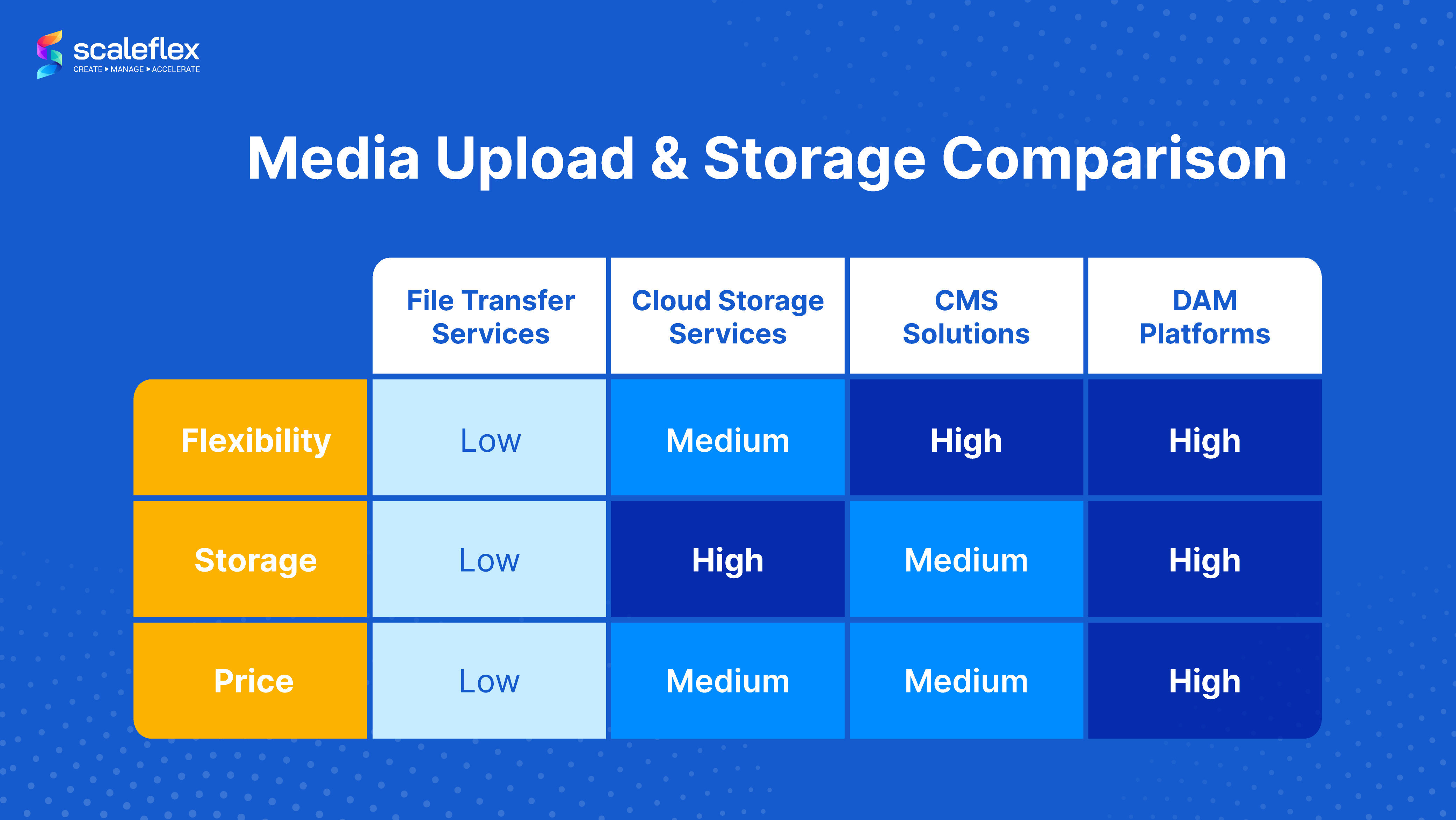
File Transfer Services
File sharing and file transfer services refer to platforms that send large files from the subscriber to the designated parties, according to the definition provided by PCMag’s encyclopedia. Some popular examples include Easyupload, Ufile, Wetransfer, Smash. Nowadays, most services provide the option to send large files exceeding file sizes attached in emails. The usual requirement is for both the sender and the recipient to have email accounts to receive notifications. However, the sender can share the download link via a messenger app. It also should be noted that file transfer services keep files on their servers for a short period of time.
Cloud Storage Services
Cloud storage refers to a cloud computing model designed to store data on the Internet with the means of a cloud computing provider. The provider is the one that manages and operates data storage as a service. The latter is delivered on-demand with just-in-time capacity and costs, thus eliminating the need of buying and managing your own data storage infrastructure.
Some of the most notable and popular examples of cloud storage services include Microsoft OneDrive, Google Drive, DropBox, and IDrive.
Digital Asset Management Platforms
We already mentioned that DAM is a great solution for companies to upload and organize their files, among other things. This type of service will help your company manage its digital assets (files), starting from their creation and upload, to publishing and archival.
Shortly said, DAMs take care of the organization and distribution of your company’s media files, visuals, content, including their upload. A neat feature DAMs have is that they can prevent duplicates. Duplicates can be a big nuisance, as they cause longer loading, more workload in management, and take more space.
Some excellent DAM providers include Scaleflex's Filerobot, Cloudinary, Bynder, Brandfolder, and Widen.
CMS and Solution Stacks
The CMS platforms (Content Management System) also offer file upload mechanisms.
A CMS is a type of software designed to manage the creation and modification of digital content. Just imagine the amount of files that CMS platforms deal with! Examples of CMS include WordPress, Wix, and Shopify. You could also roll out your own file upload solution using an appropriate stack of tools for the different layers. Such tools could be MySQL, PHP, Python, JavaScript, Angular, and React.
Conclusion
If you’ve ever asked the question “How Do I Upload Files?,” we hope that we covered for you all the file upload options available today for both home users and various-sized companies. However, if we have to point to one solution that best optimizes the upload media process, we’d say that DAMs such as Filerobot are the right choice for organizing your digital files in an enterprise environment.
With Filerobot, you can store, process, share and accelerate various types of files on both web and mobile applications. The platform allows you to manage all your media assets in 4 easy-to-follow steps: manage, process, accelerate, and monitor. Its easy-to-use file and image uploader plugin can be integrated within minutes with just a few lines of code! We invite you to learn more about how you can implement Filerobot in your workflow.
FAQs
Where can I upload files for others to download for free?
Today, it’s quite easy to share your files with everybody. You can use file sharing and storage services for this purpose. Examples include Microsoft OneDrive, Amazon Drive, JumpShare, Hightail, and MediaFire.
How do I upload a file and share it?
Depending on the service you want to upload media with, you will need to complete several steps, usually similar in their nature. Usually, the first step involves choosing the file you need to share. Then, you need to select and upload it to the media uploader. Once the process is finished, all you need to do is share the download link.
How can I send large files?
Large file sharing can be accomplished. For example, you can upload your files to a cloud storage space, such as Google Drive, Dropbox, or OneDrive. Then, you can share or email them. Another option is using file compression software, such as 7-Zip, which is a free compression software. It enables you to send a folder full of files at once. You can also rely on free online services, such as Jumpshare. It lets you send up to 250 MB with a free account. All you need to do is upload the files and share the link.
Which file-sharing site is the best?
There isn’t a certain answer to this, as it solely depends on the actual use case. In this article, we have covered the best options available for users today. Both giants like Dropbox, Box, Google, Microsoft, and smaller vendors such as MediaFile, provide online storage options, including file sharing, file synchronization across your various devices, and even collaboration features.
What is the difference between digital asset management and cloud storage?
DAMs can organize your content in a way that cloud storage providers can’t. The biggest difference between a DAM and a cloud platform is that the first one is oriented towards the media assets, whereas the second one is centered on the user. Furthermore, DAMs are usually used for collaboration, meaning that they provide access to various people. Cloud storage, on the other hand, is more privacy-oriented.
Return to the Table of Contents



